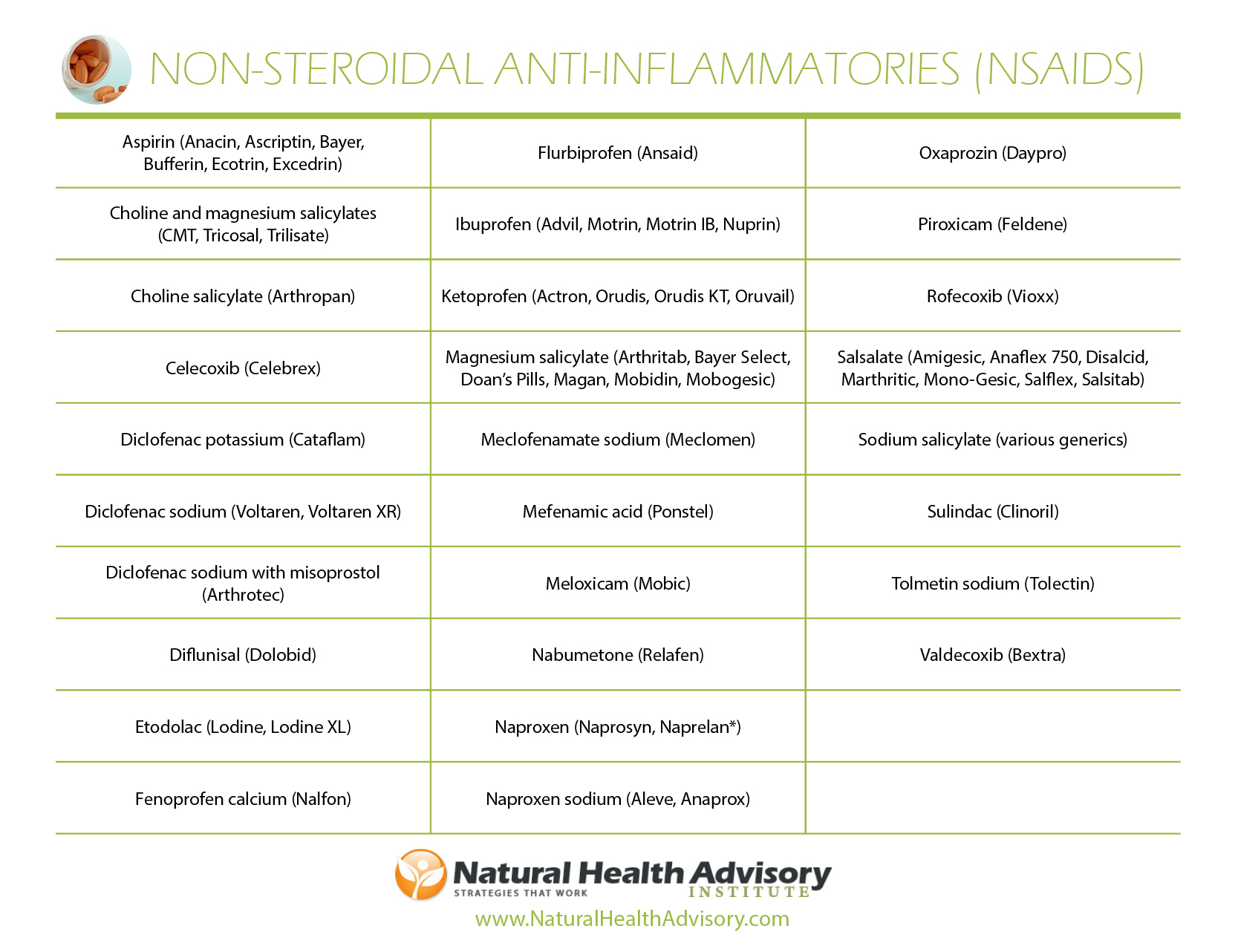
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, are a class of drugs that reduce swelling, reduce inflammation, relieve pain, lower fever, reduce blood clots, and lower cholesterol at lower doses. NSAIDs are usually taken in combination with aspirin to reduce pain and reduce the risk of bleeding.
Non-steroidal NSAIDs can cause several side effects, including stomach ulcers, diarrhea, stomach bleeding, abdominal edema, stomach or duodenal ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, and liver damage. Some of these side effects are usually temporary, while others are not.
There are many ways to combine NSAIDs with aspirin to treat pain and reduce inflammation. Aspirin is an analgesic, which means that it blocks pain signals to the brain by binding to receptor sites. NSAIDs block receptors on the skin, which allows the body to produce fewer pain-causing chemicals. They also cause a decrease in platelet production, an increase in prothrombin time (protein synthesis), and a decrease in the ability of platelets to heal wounds.
Some doctors prescribe NSAIDs along with other medicines for patients who have chronic joint pain and who may benefit from these drugs. However, NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with a history of comorbidities such as heart disease, kidney disease, heart problems, liver problems, diabetes, cancer or liver disease.
Ibuprofen is also known as motrin and is sometimes combined with aspirin to reduce pain and inflammation in patients with arthritis. Ibuprofen is available without a prescription. It is available in pill form. You can take one tablet a day for several days to weeks. Your doctor will recommend the dosage and medications to take based on your specific condition.
If you need to reduce inflammation or if you have joint pain in other parts of your body, you may want to consider taking two or three pain relievers. Ibuprofen is usually effective for reducing pain, swelling, redness, stiffness, and soreness, but it may not be effective for relieving arthritis pain, rheumatoid arthritis pain, or osteoarthritis pain.
To avoid serious side effects, take ibuprofen with caution if you experience chest pain, heartburn, nausea, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, blurred vision, vomiting, or upset stomach. or if you have unusual bleeding or bruising. Ibuprofen should be used with caution in pregnant and nursing women, women with liver problems, or women who are breastfeeding. Do not take ibuprofen for more than three months at a time, as it may cause the uterus to contract. Also, it should not be taken if you have any underlying medical conditions.
Ibuprofen should only be taken for short periods of time if you have a medical condition and should not be taken for long-term use. Ibuprofen is very damaging to the stomach, so use it with caution. Also, avoid using products containing aspirin or ibuprofen if you have liver or kidney problems. If you have been prescribed a course of NSAIDs (such as Alka-Seltzer), take it as directed on the label.
NSAIDs slow down the production of digestive juices, making stomach acids more volatile and therefore less effective at removing fat from the stomach. This makes it easier for stomach fat to leak and form ulcers and other health problems.
Ibuprofen can also cause serious side effects such as stomach ulcers, vomiting, diarrhea, and even heart problems. if you are prone to high blood pressure, stomach problems or anemia, or if you have diabetes or kidney disease. only use it with caution. It should never be used on a regular basis for a long time. In some cases, a course of ibuprofen can harm infants and children, as well as pregnant women.
People with liver or kidney problems should avoid long-term use of NSAIDs. If you have ever had stomach ulcers, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, do not take ibuprofen.
Leave a Reply