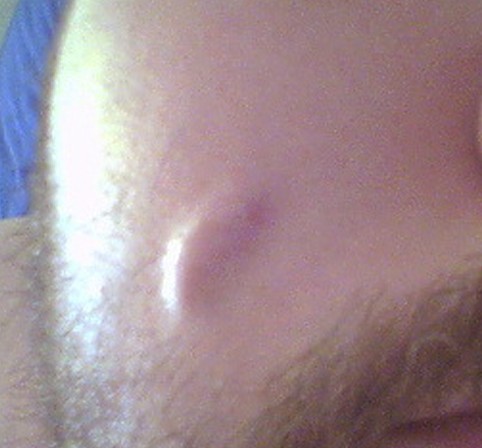
The most common types of cysts are epidermoid and ganglion. Both form in the top layer of skin and are filled with dead skin cells. Bacteria break down these cells, resulting in the buildup of the cyst. Pilar cysts are similar to epidermoid cysts, but only form on the scalp. There is no known cause for either type of cyst, though the former tends to be smaller.
Kidney cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs in the kidney. Some are congenital, while others are acquired. Choroid plexus cysts are pinched off blebs filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Aneurysmal cysts form in a vein or other structure, and contain neoplastic cells. Acne cysts are usually asymptomatic, but may develop into an abscess when they are pus-filled.
The most common cyst types are sebaceous and epidermoid. The most common types of these cysts form under the skin, and are called epidermoid and sebaceous. The causes of these types of cysts are unknown, but they are generally triggered by a blockage in a duct. The cause can be inherited or caused by infection. The most common sites where cysts form are the ovaries, breast, and kidney.
Surgical removal of an obstructing cyst is the most common treatment for a symptomatic cyst. However, there are other ways to treat a symptomatic cyst, such as a topical cream or an ointment. Surgical removal of a bacterial or parasitic infection is the most common medical treatment, but some cysts are more serious and may require a doctor’s care. While the majority of cases are benign, some may cause complications. During the treatment process, the patient is prescribed medication that may be used to treat the condition.
If a bacterial infection has caused the cyst, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. It can spread throughout the body and lead to further complications. Infections of the pelvic area can lead to a bacterial infection of the ovaries, affecting the ovary. The presence of a bacterial infection can cause a cyst to form on the ovaries. A recurring cyst can lead to complications, including a complication related to menstrual pain and discomfort.
An ultrasound can detect an ovarian cyst. The physician may notice a swelling on the ovaries. After identifying the type of cyst, the doctor may order an ultrasound test. The ultrasound can show the size, location, and composition of the cyst. Most cysts resolve on their own after a few weeks, but it is best to get a second opinion. These tests are not life-threatening. You should not be concerned about the size or location of the cyst. It will disappear on its own.
Although most people go to their family doctor for medical problems, you can also consult with your doctor. Your family doctor is best placed to diagnose and treat the cyst. Most likely, they will conduct a thorough examination and suggest appropriate treatment. If the cyst is infected, antibiotics may be needed. Most cysts are benign, so there is no reason to worry about this. If you suspect a cyst, make sure it is not too large.
Surgical removal may be an option for women who experience persistent pain and discomfort from the cyst. In some cases, the cyst may be cancerous and require surgery. Most people experience no symptoms during surgery, but there are many risks involved. The procedure can be a risk factor for ovarian cancer, so it’s important to discuss it with your doctor. If a cyst is found, it must be removed.
A cyst can cause various symptoms in a woman. Herbs and hormones can contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts. Although these symptoms are usually minor, you should not ignore any lumps or cysts. Most of them will disappear on their own. Your doctor may schedule regular checkups to keep you under control and prescribe medications that can help relieve discomfort. If you have been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst, you can consult with your doctor and at Productos de Salud en Argentina to get a diagnosis and treatment.
Although most cysts cannot be prevented, some can be prevented. Fortunately, you can prevent the development of infections that can lead to ovarian cysts. An acute pelvic infection can spread to the ovaries, increasing the risk of ovarian cysts forming in the body. For example, a severe pelvic infection can spread to the egg, which is a common cause of ovarian cysts. Even if you don’t know about the symptoms, a doctor can do a simple test to determine the cause.
Leave a Reply